BannerBio was invited to participate in the Food Tech Innovation Salon “New Food Generation" organized by Innolink on July 16, 2021.
Dr.Xi Zhang, the General Manager of BannerBio, made a speech with topic "The Second Domestication of Microorganisms - The Innovative Applications and Value of Fermented Protein". She elaborated the role played by microbial fermentation in the field of alternative protein and its future application potentials.

First, Dr. Zhang briefly introduced some basic knowledge about microorganisms: the tiny creatures invisible to human eyes are categorized into various different types, including fungi, bacteria, viruses, and algae. Microorganisms are also double-edged sword: on the one hand they bring us colorful lives and help us maintain ecological balance; on the other hand they could cause food corruption and many diseases.
For thousands of years, humans have used fermentation technology to make a variety of foods, which is the first domestication of microorganisms.

Then Dr. Zhang shared three common methods to utilize microorganisms, which we called the “second domestication”
The first is traditional fermentation. We can carry out refined extraction through strain selection, temperature adjustment, pH value, dissolving ocean, etc. The second is biomass fermentation, which takes advantage of the exponential growth of microorganisms to collect and use. The third type is precision fermentation, which refers to the collect and use of secondary metabolites produced in the process of microbial fermentation.
The second domestication has relatively mature applications in other industries. For example, in the biological manufacturing industry, the commonly used antibiotics (such as penicillin and streptomycin) are secondary products produced by the fungus Penicillium and the bacterial Streptomyces. There are also many high-quality products for fermentation applications of synthetic biology, such as succinic acid, alanine in the chemical industry, inositol, levodopa, vitamin B12 in the raw material field, and ginsenosides/ lycopene, gastrodin in plant ingredients.
Finally, Dr. Zhang focused on the advantages and applications of fermented protein in the field of alternative protein.
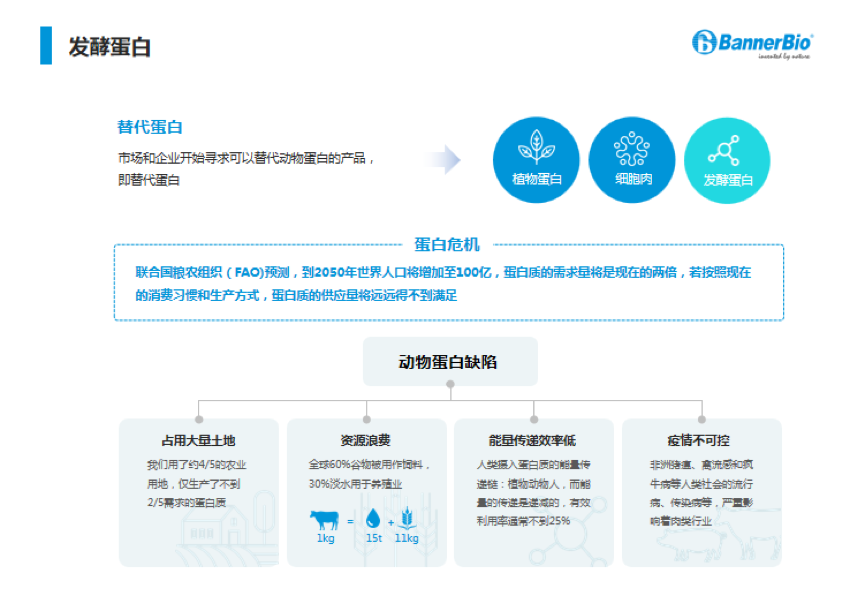
The alternative protein we usually talk about includes three sources: vegetable protein, cell meat, and fermented protein. The main advantages of fermented protein are: 1. High production efficiency. The production cycle of animals and plants can take up to several months or years, while the duration for microbes to multiply is often several hours or days. 2. It overturns the traditional agricultural model and adopts an industrial model for production, which compares to traditional agriculture, only uses single-digit percentages of land, carbon and water. 3.Excellent value. The nutritional structure of protein currently disclosed is no less than that of plant protein and animal protein.
Fermented protein is a new ingredient which can replace animal and plant protein to a certain extent. For example: Quorn (founded in 1985), the first company that produced fermented protein for meat substitutes, used a microbial strain called Fusarium. This strain was discovered as early as 1967, and the meat substitutes of fermented protein began to be sold in the UK in 1993, in the USA and Australia in 2002 and 2010 respectively.
Nature’s Fynd uses Fusarium discovered in the Yellowstone National Park. The founder, Thomas Jonas discovered this strain during the excavation of extreme environmental microorganisms. Later he founded the company Nature’s Fynd in 2013 which was subsequently funded by the U.S. government from 2013 to 2018. Capital entered in 2019, investors include Bill Gates, Bezos, etc, and up to now, it has completed financing of 350 million US dollars and started large-scale production.

After the speech, the invited guests held a discussion session to share their insights of the food technologies and commercial trends in the future.
Tel: 0755-26504868 (China)
Tel: 1-909-921-0808 (USA)
Email: sales@bannerbio.com
Wechat ID: bannerbio
Copyright © BannerBio Nutraceuticals Inc., All rights reserved.
